Lec 16 - Supplemental Reeb Graph Examples#
To see some examples, we will use the ceREEBerus package.
# Run in case you don't already have it installed:
# pip install cereeberus
# Note you need at least version 0.1.9 of ceREEBerus due to updates in naming conventions.
from cereeberus import ReebGraph, LowerStar, computeReeb
from cereeberus.data.ex_torus import Torus
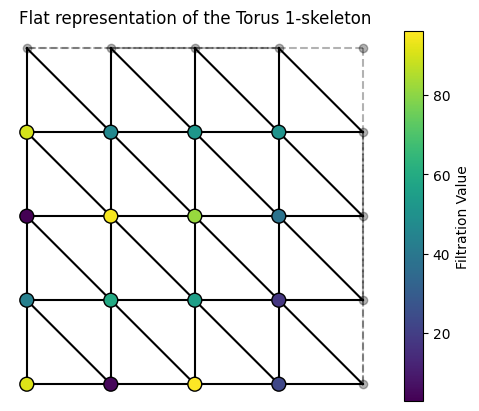
The example we’ve been using in the class lecture can be coded as follows. Notice that because my triangles in the code are backwards from the figures from class, this is actually a mirror image of that representation.
T = Torus()
T.generate_grid(grid_size = 4)
# f = {3:11, 2:13, 1:15, 0:7,
# 7:14, 6:1, 5:3, 4:16,
# 11:9, 10:2, 9:4, 8:8,
# 15:10, 14:12, 13:6, 12:5}
# for v in f.keys():
# T.assign_filtration(v, f[v])
T.assign_random_values(1,100)
T.draw()
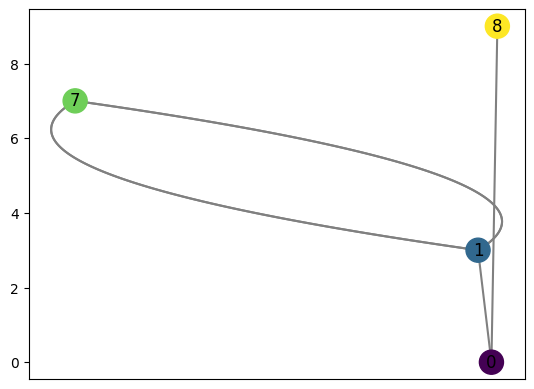
Then to compute the Reeb graph of this torus, we have the following.
R = computeReeb(T, verbose = False)
R.remove_all_regular_vertices()
R.draw(cpx = 3)
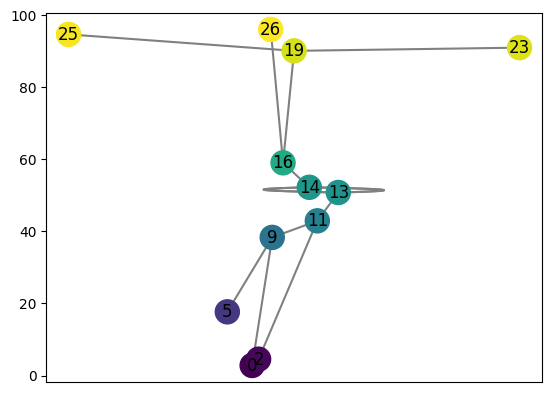
Second example#
Consider the following example:
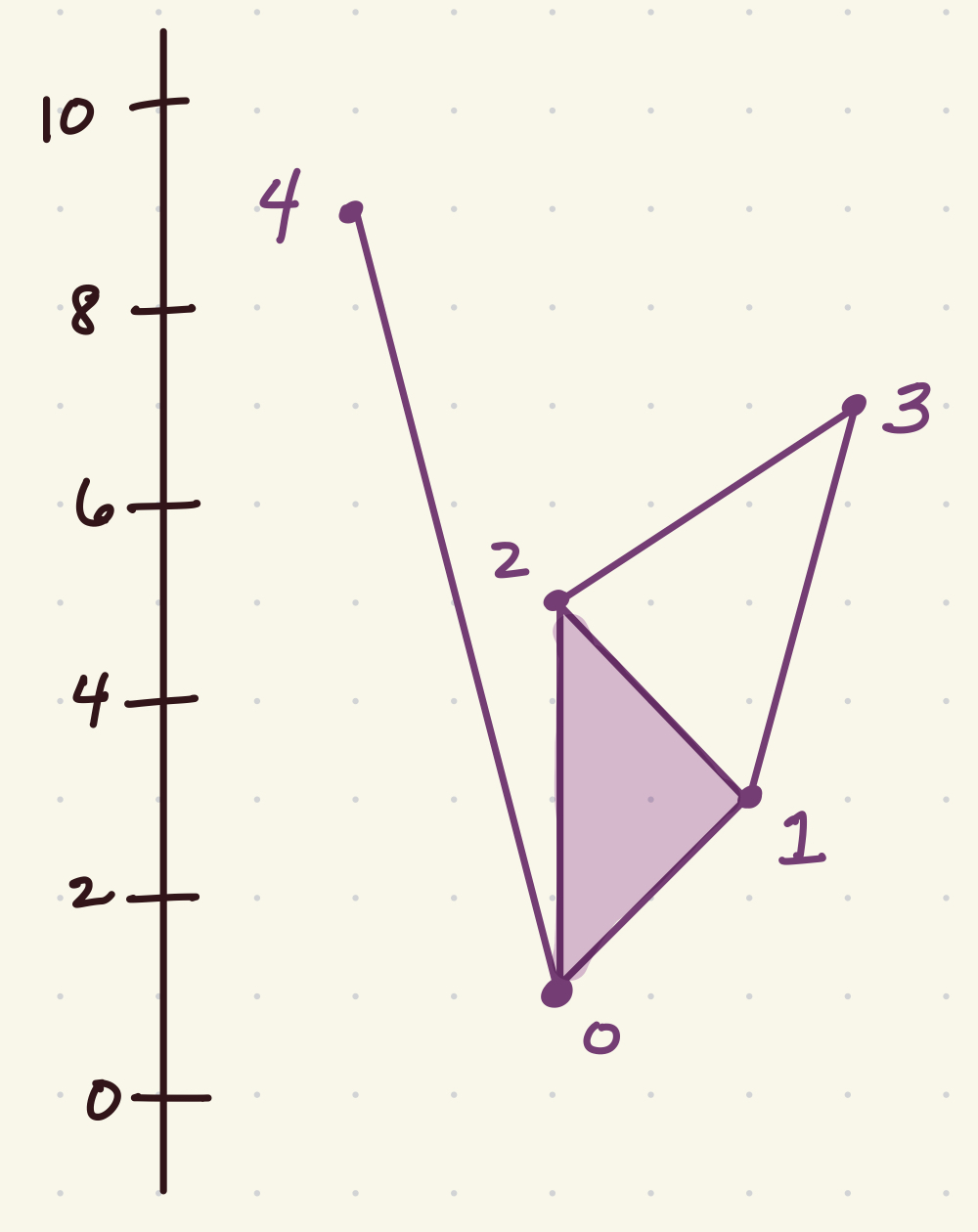
Below is the code to store this filtration. Note that I don’t need to specify every simplex, just the top dimensional ones.
K = LowerStar()
# Add top dimensional simplices
K.insert([0, 1, 2])
K.insert([1, 3])
K.insert([2,3])
K.insert([0,4])
# Assign filtration values to vertices
K.assign_filtration([0], 0.0)
K.assign_filtration([1], 3.0)
K.assign_filtration([2], 5.0)
K.assign_filtration([3], 7)
K.assign_filtration([4], 9.0)
Do this: Compute the Reeb graph of this filtration. Is it the same as what you computed by hand in class?
# your code here
R = computeReeb(K)
R.remove_all_regular_vertices()
R.draw(cpx = 3)